Whether you’re simply flirting with the concept of repairing your own credit or you’re ready to jump in with both feet today, do yourself a favor.
Take a couple of moments to read over the credit repair terms you’ll see throughout the process. Although everything doesn’t sink in immediately,
you’ll have given yourself a solid jumpstart that may make every subsequent step feel less daunting and more familiar.
Credit repair – The method of improving your credit. Though you can pay a credit repair company to try and do the work for you, it’s something you’ll
be able to do it at no cost on your own.
Credit scores – This’s a number that is used by creditors to determine your creditworthiness. An algorithm generates these scores. This score is used to interpret the credit
Reports compiled by credit reporting bureaus. The goal of credit repair is to improve credit score numbers.
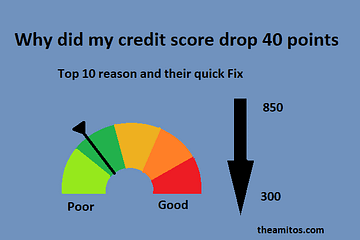
Both the FICO and Vantage Scores range from 300 to 850, broken down as follows:
- 750-850 – Excellent
- 650-749 – Good
- 600-649 – fair
- 300-599 – Poor
Industry-specific FICO scores range from 250 to 900.
FICO Score – This is often the credit score that a reported ninety percent of creditors use when assessing your creditworthiness. you have got multiple FICO Scores specific to the type of credit you may be seeking, including
Totally different versions of auto loans, credit cards, and mortgages. you’ll be able to purchase your FICO Scores through myFICO.com.
Vantage Score – this is a score created by the three major credit-reporting bureaus in 2006, to compete with the FICO score. you can purchase your Vantage Scores through Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax.
Credit reports – this report contains the record of your credit history, together with credit inquiries, credit accounts, balances, credit limits, timeliness of payments, accounts in collections, and some public records also included (e.g., wage garnishment, tax liens, bankruptcies, foreclosures, lawsuits, judgments). Creditors usually look at your credit reports, also because of the credit scores that the reports generate. That’s why looking over your credit reports is the first step in the credit repair method.
The only method of cleansing them up knows what’s on there. you’ll be able to see your credit reports every twelve months through AnnualCreditReport.com.
Credit reporting bureaus – The agencies that collect and update your credit history into credit reports. Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax are the three main credit-reporting bureaus. All three agencies have separate credit reports on you; therefore, it’s necessary to check all three.
Credit report dispute – The action you’re taking to challenge an error that you just notice on your credit report. Although every credit bureau has an online dispute method, it’s suggested that you just dispute the error in writing and send it via certified mail with the return receipt requested.
Debt validation – The action you’re taking to challenge an old debt that has been turned over to a collection agency or purchased from the original creditor by a debt buyer. Once you request debt validation, the law needs the collector, to verify the debt, as well as their right to collect on it. If such proof cannot be provided, you’re not needed to pay the debt and therefore the listing should be removed from your credit reports.
Secured credit card – A credit that needs a cash deposit. Generally, the amount of the deposit is up to the credit line. Once you have improved your credit score, you should upgrade the secured credit card to a regular credit card otherwise you might apply for a new one through a different issuer.
Get started repairing your credit today!


0 Comments